RC Circuits: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[File:RC example graph.png|left|400px]] | [[File:RC example graph.png|left|400px]] | ||
<br class="clear"/> | <br class="clear"/> | ||
<div style="clear:both;"></div> | |||
= Videos = | = Videos = | ||
| Line 51: | Line 52: | ||
<br class="clear"/> | <br class="clear"/> | ||
Back to [[Electricity_and_Magnetism]] | Back to [[Electricity_and_Magnetism]] | ||
<br class="clear"/> | |||
Next: [[Magnetic Fields]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:50, 22 November 2024
Back to Electricity_and_Magnetism
Textbook
What is a Capacitor and what is Capacitance
See Capacitors
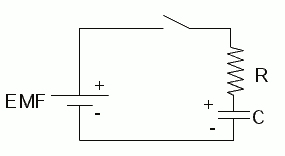
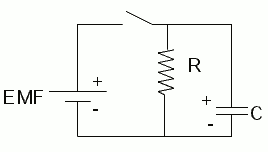
RC Circuits
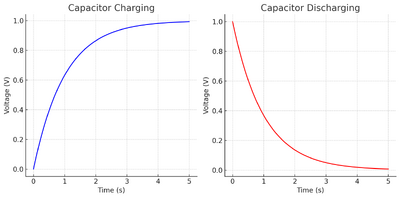
Capacitor Charging (Voltage over Time)
During charging, the voltage across a capacitor increases exponentially, approaching its final value.
- Where:*
- *V(t)* is the voltage at time t (in volts, V)
- *V_0* is the final voltage (in volts, V)
- *R* is the resistance (in ohms, Ω)
- *C* is the capacitance (in farads, F)
- *t* is time (in seconds, s)
Capacitor Discharge (Voltage over Time)
During the discharge of a capacitor through a resistor, the voltage decreases exponentially over time.
- Where:*
- *V(t)* is the voltage at time t (in volts, V)
- *V_0* is the initial voltage (in volts, V)
- *R* is the resistance (in ohms, Ω)
- *C* is the capacitance (in farads, F)
- *t* is time (in seconds, s)
Example Graphs
Videos
Simulations
Other Links
Back to Electricity_and_Magnetism
Next: Magnetic Fields